中文摘要
本文介紹了眼球屈光不正的相關問題及其治療方法。
眼球屈光不正是一種常見的視覺問題,包括近視、遠視和散光。
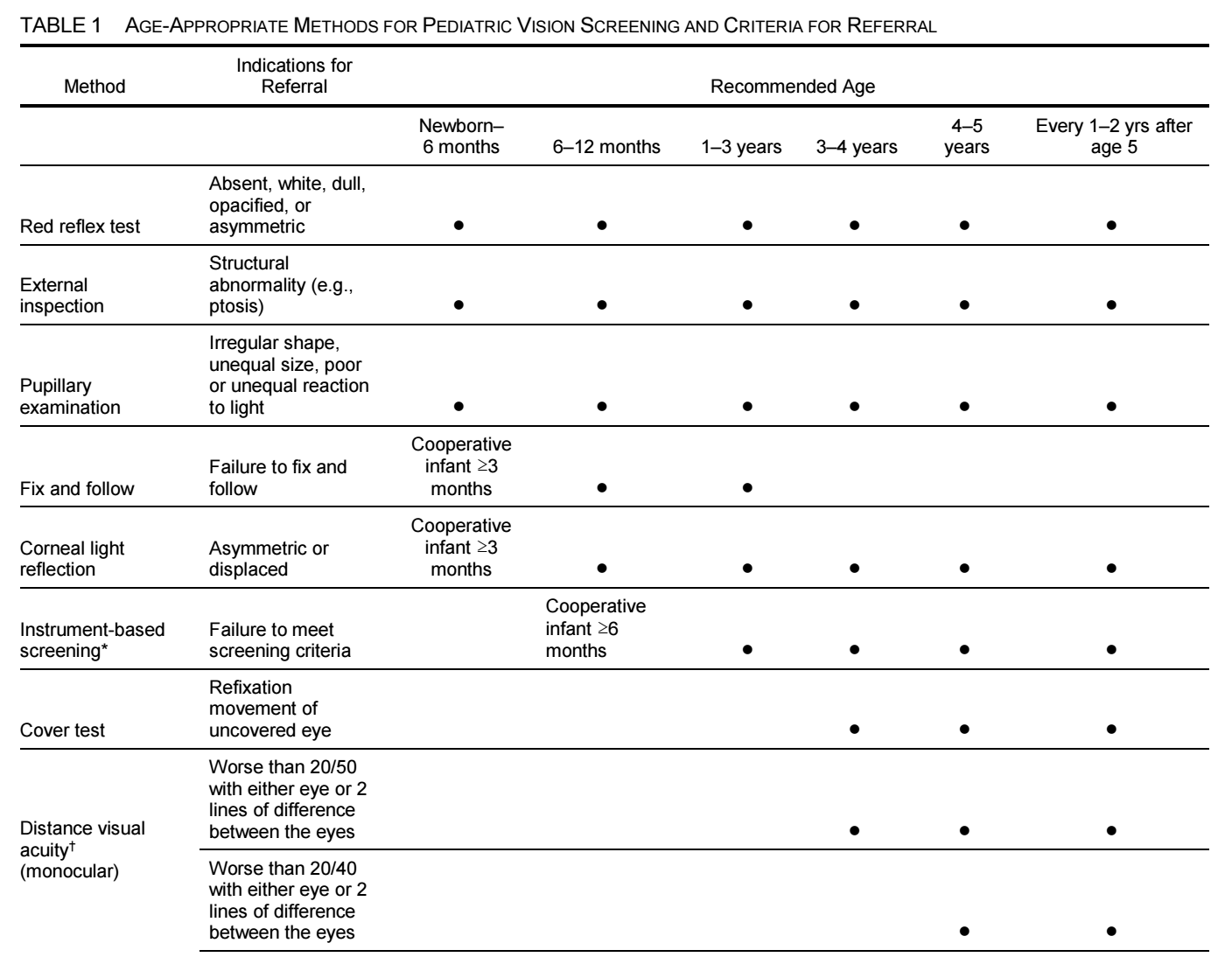
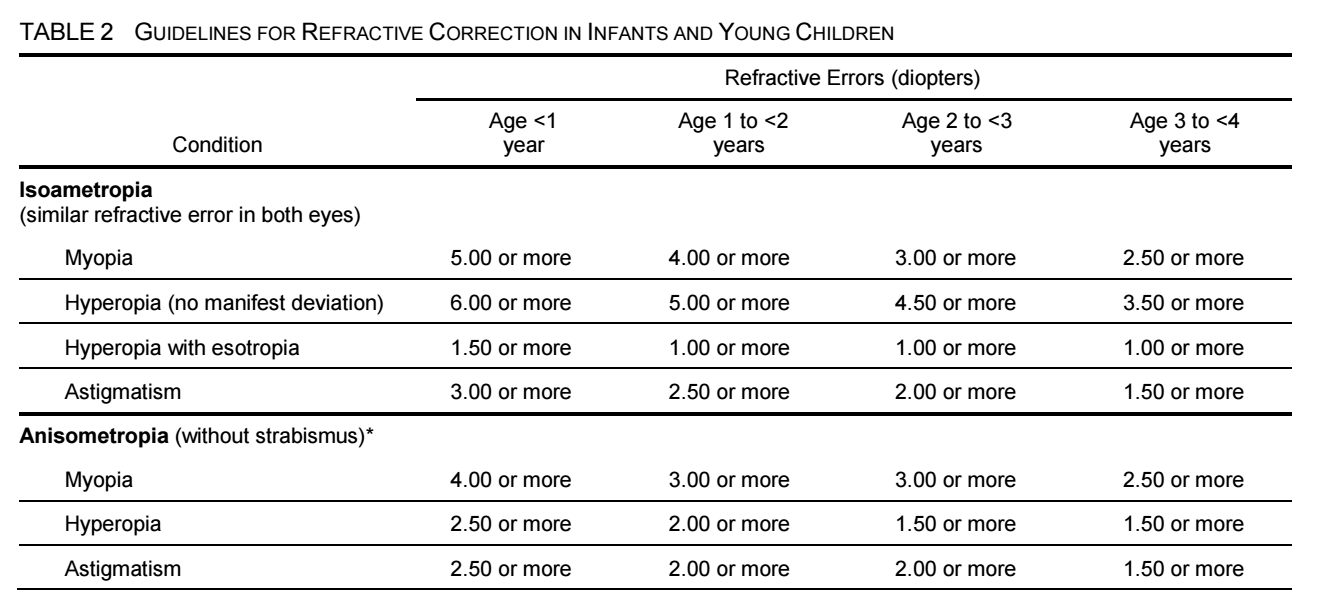
視力檢查和眼科檢查對於確定屈光不正的診斷和治療方案至關重要。矯正視力是診斷和治療眼球屈光不正的首要方法,以提高視力和減少不適感。選擇適合的眼鏡鏡框和鏡片對於矯正視力非常重要。
隱形眼鏡是另一種矯正視力的方法。在隱形眼鏡的選擇方面,應考慮患者的生活方式和需要。在安全和舒適性方面,目前的隱形眼鏡比過去有很大的改進。在選擇隱形眼鏡之前,應該進行完整的眼科檢查,以確定是否適合使用隱形眼鏡,以及適合哪種類型的隱形眼鏡。
在隱形眼鏡的使用中,適當的保養和清潔非常重要。不遵從隱形眼鏡的建議使用方法和保養方法,可能會導致角膜損傷和感染。在使用隱形眼鏡時,患者應注意眼睛是否有不適感,如灼熱、疼痛、視力模糊、紅斑和分泌物等。
有關角膜炎的研究顯示,Pseudomonas為使用隱形眼鏡相關的角膜炎最常見的病原體,而兒童的微生物性角膜炎風險相對較高。角膜炎風險增加的原因包括使用同一隱形眼鏡超過規定期限、隱形眼鏡清潔不當以及睡覺時未取出隱形眼鏡。在診斷和管理隱形眼鏡相關的問題時,醫護人員需要進行全面的眼科評估,包括評估患者的角膜和眼表,並詢問患者有無相關問題,例如眼睛紅腫、疼痛或異物感。
另一方面,鑑於許多人需要眼鏡或隱形眼鏡進行視力矯正,建議對於眼科醫生和患者,掌握當前的矯正方法以及各種矯正方法的適應症和禁忌症。
眼科醫生需要對不同人群的矯正方式進行全面的評估,包括患者的年齡、病史、角膜形態、視力問題的嚴重程度以及患者的職業和活動需求。例如,對於青少年和兒童,尤其是那些有近視風險的人,可以採用對抗近視進展的治療方法,如使用矯正光學和配戴角膜塑形鏡片等。
對於老年人或其他需要視力矯正的人,可以考慮使用多焦點鏡片或漸進式眼镜等多種矯正方法,以滿足他們不同距離的視力需求。此外,RGP lenses 是治療高度近視和高度散光的有效方法。需要指出的是,醫生在選擇矯正方法時應注意患者的眼睛健康和安全,以避免出現相關併發症。
English Abstract
This article discusses the related issues and treatment methods for refractive errors of the eye. Refractive errors of the eye are a common vision problem, including myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Vision and eye examinations are essential for determining the diagnosis and treatment plan for refractive errors. Correcting vision is the primary method for diagnosing and treating refractive errors of the eye, to improve vision and reduce discomfort. Choosing the appropriate eyeglass frames and lenses is critical for correcting vision.
Contact lenses are another method for correcting vision. In selecting contact lenses, patients’ lifestyles and needs should be considered. In terms of safety and comfort, current contact lenses have greatly improved compared to the past. Before selecting contact lenses, a complete eye examination should be conducted to determine if contact lenses are suitable and which type of contact lenses are appropriate.
Proper maintenance and cleaning are essential for contact lens use. Failure to follow the recommended usage and maintenance methods for contact lenses may lead to corneal damage and infection. When using contact lenses, patients should pay attention to any discomfort, such as burning, pain, blurred vision, redness, and discharge.
Research on keratitis shows that Pseudomonas is the most common pathogen associated with contact lens-related keratitis, and children are relatively more at risk for microbial keratitis. The reasons for increased risk of keratitis include using the same contact lenses beyond the prescribed time frame, improper contact lens cleaning, and failure to remove contact lenses while sleeping. When diagnosing and managing contact lens-related problems, healthcare professionals need to conduct a comprehensive eye assessment, including evaluating the patient’s cornea and ocular surface, and inquire about any relevant issues such as eye swelling, pain, or foreign body sensation.
On the other hand, considering that many people require glasses or contact lenses for vision correction, it is recommended for ophthalmologists and patients to be familiar with the current correction methods and the indications and contraindications for various correction methods. Ophthalmologists need to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the correction methods for different populations, including the patient’s age, medical history, corneal morphology, severity of visual problems, and the patient’s occupation and activity needs. For example, for adolescents and children, especially those at risk for myopia, treatment methods to counteract myopia progression, such as using correcting optics, and wearing orthokeratology lenses, can be used.
For elderly individuals or others who require vision correction, various correction methods such as multifocal lenses or progressive eyeglasses can be considered to meet their visual needs at different distances. Additionally, rigid gas-permeable contact lenses are an effective method for treating highly myopic and highly astigmatic conditions. It should be noted that doctors should pay attention to patients’ eye health and safety when selecting correction methods to avoid related complications.
HIGHLIGHTED FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CARE
The prevalence of myopia is increasing in the United States and other industrialized societies. Increased time spent outdoors appears to be protective against myopia in children. Increased levels of near work are less of a risk factor than previously believed.
Increased outdoor time and low-concentration atropine have been shown to reduce the likelihood of myopia onset.
Antimuscarinic eyedrops, multifocal spectacles and contact lenses, and overnight orthokeratology have been shown to be varibly effective in some populations for myopia control, that is, to reduce the progression of myopia in school age children.
Studies from around the world have confirmed that that the incidence of microbial keratitis has not been reduced with the introduction of new lens types and that overnight wear of any contact lens is associated with a higher risk of infection than daily wear.
Although there are lenses approved by the FDA for extended wear, alternatives should be presented to patients for whom this mode of contact lens wear is being considered because overnight wear, regardless of contact lens type, increases risk of microbial keratitis.
Daily disposable contact lenses (rather than planned replacement lenses) are the safest lenses with the lowest rate of complications associated with soft contact lens wear. No-rub cleaning, topping off (reuse) of solutions, contaminated lens cases, exposure to tap water, wearing contact lenses in hot tubs and showers and while swimming, and changes in water supply are associated with Acanthamoeba and fungal keratitis related to contact lens wear in the recent decades.
Hydrogen peroxide systems are superior to multipurpose solutions for reducing the likelihood of infections or inflammatory complications; they are the preferred mode of nightly disinfection for patients who cannot wear daily disposable lenses, especially if they have had complications of contact lens wear in the past.
Presbyopia can be managed by using eyeglasses; contact lenses; topical agents; intraocular lenses with multifocal, accommodating, or extended depth of focus features; and monovision strategies with contact lenses or intraocular lenses. Adverse events related to FDA-approved drugs and devices should be reported to MedWatch
(www.fda.gov/medwatch)